Our Species

With Disruptive Conservation, We Can Save Animals & Their Ecosystems

With Disruptive Conservation, We Can Save Animals & Their Ecosystems
For the first time ever, humanity possesses the means to rectify our past missteps and heal nature on a massive scale. By building on the knowledge and successes of the conservationists that came before us, and utilizing breakthroughs in science and technology, we have an opportunity to turn the tide on extinction and secure a vibrant future for life on Earth.
At Colossal, nothing is more important than supporting species, balance and biodiversity in our planet’s ecosystems. That’s why our conservation efforts are ambitious and intentionally engineered to drive the development of technologies for the benefit of the future.
species Lab
& field notes

 African & Asian Elephants
African & Asian Elephants
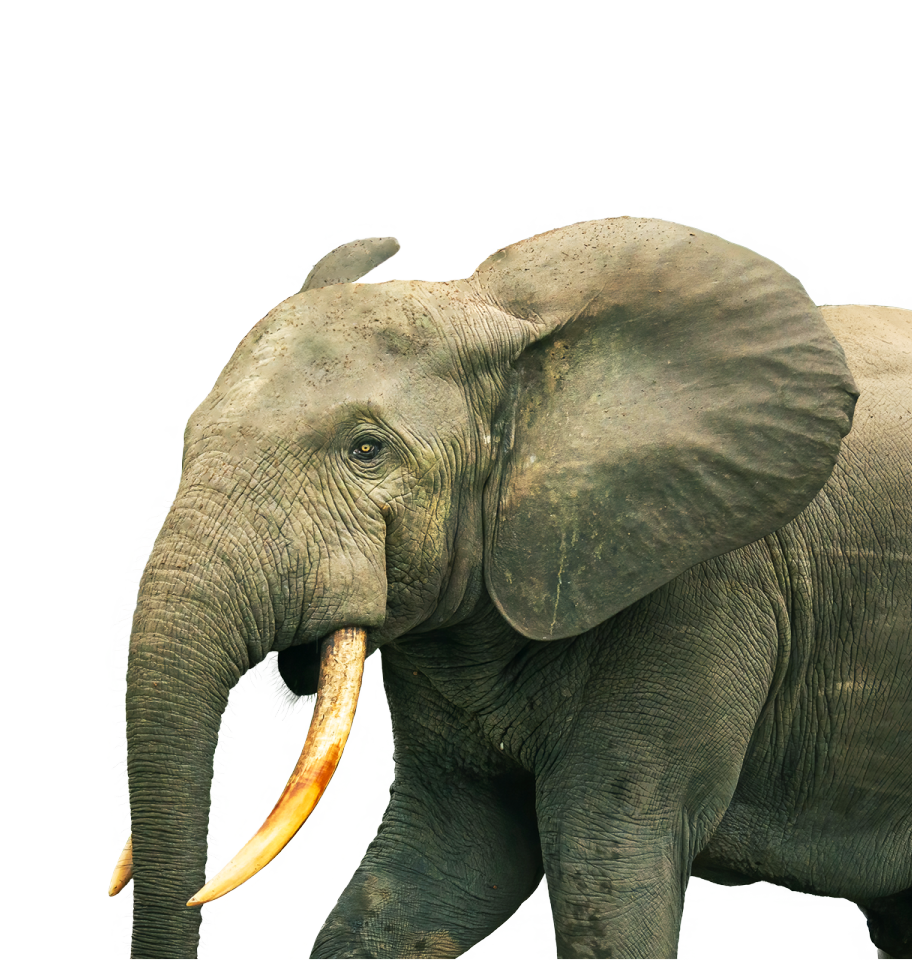


African Forest Elephants
Loxodonta cyclotis
- Est. Current Population: 95,000
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Proboscidea
- Family: Elephantidae
- Genus: Loxodonta
- Region: West & Central Africa
- Avg. Weight: Up to 4,000 kg
 [ Status : Critically Endangered ]
[ Status : Critically Endangered ]

Population Threats
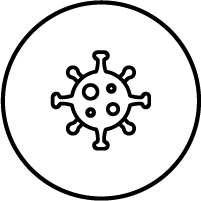 EEHV
EEHV Habitat Loss
Habitat Loss Poaching
Poaching Human-Elephant Conflict
Human-Elephant Conflict


African Savanna Elephant
Loxodonta africana
- Est. Current Population: 350,000
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Proboscidea
- Family: Elephantidae
- Genus: Loxodonta
- Region: Sub-Saharan Africa
 [ Status : ENDANGERED ]
[ Status : ENDANGERED ]


Population Threats
 EEHV
EEHV Habitat Loss
Habitat Loss Poaching & Wildlife
Poaching & Wildlife Human-Elephant Conflict
Human-Elephant Conflict


Asian Elephants
Elephas maximus
- Est. Current Population: <50,000
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Proboscidea
- Family: Elephantidae
- Genus: Elephas
- Region: Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia
- Avg. Length: 5.5–6.5 m (including trunk)
- Avg. Weight: 2.7 - 4 tons
 [ Status : Endangered ]
[ Status : Endangered ]


Population Threats
 EEHV
EEHV Habitat Loss
Habitat Loss Poaching
Poaching Human-Elephant Conflict
Human-Elephant Conflict
Our Programs
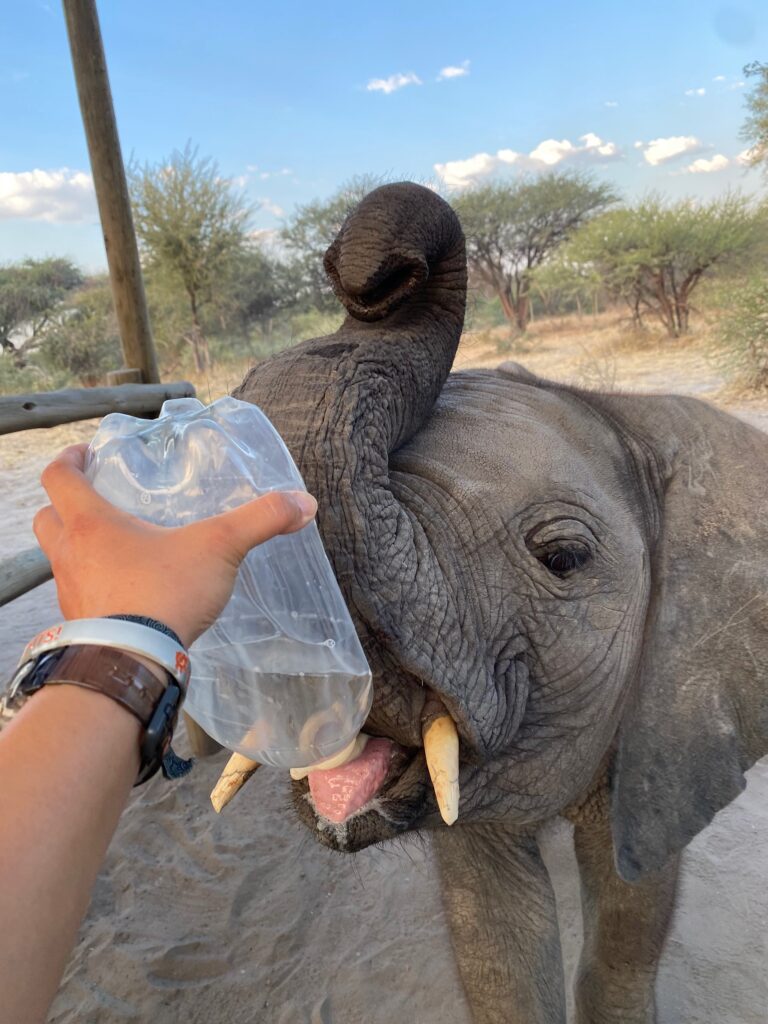

In Partnership With:

AI-Enhanced Orphan Elephant Reintroduction
Partnering with Botswana’s Elephant Havens, we employ our AI platform to study orphaned elephants’ social development for eventual reintroduction. This aids Elephant Havens’ release strategies and provides valuable insights for rewilding elephants in herds lacking a strong adult presence.
Learn More
In Partnership With:

Elephant Drone Behavior Tracking
Deciphering the secrets of elephant behavior could revolutionize conservation for this iconic species. This project utilizes advanced drone technology and machine learning for tracking and studying African elephants, and aims to enhance conservation and research efforts by providing detailed insights into elephant behavior and social dynamics.
Learn More
In Partnership With:

Saving Elephants from a Deadly Virus
Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpes Virus (EEHV) is a leading cause of death among juvenile elephants worldwide. This project aims to combat EEHV by developing vaccines and treatments to protect both captive and wild elephant populations.
Learn More

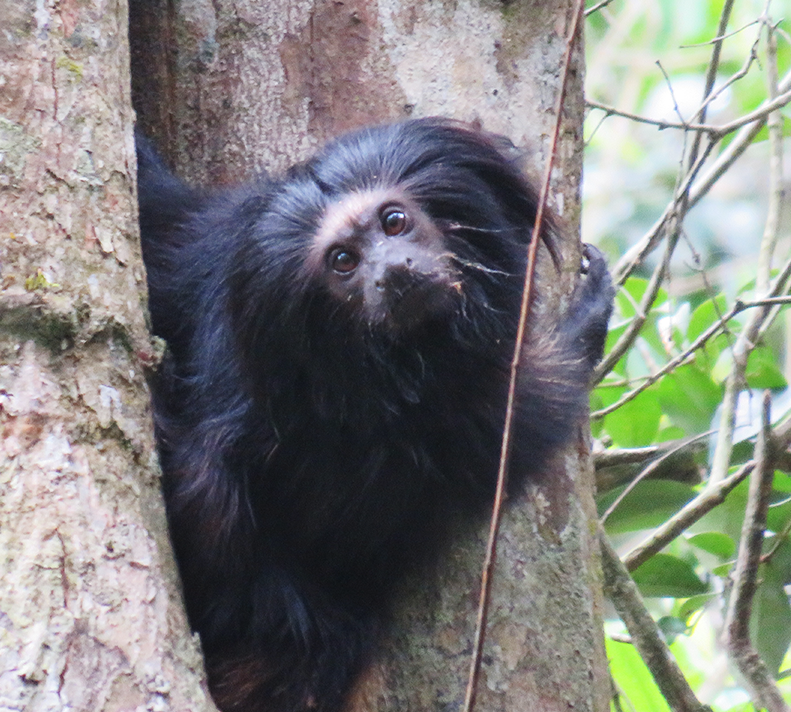
Black Lion Tamarin
Leontopithecus chrysopygus
- Estimated Population: Less than 1,600
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Primate
- Family: Callitrichidae
- Genus: Leontopithecus
 [ Status : Endangered ]
[ Status : Endangered ]


Population Threats
 Habitat Loss
Habitat Loss Illegal Pet Trade Pressures
Illegal Pet Trade Pressures Genetic Diversity
Genetic Diversity
Our Programs

In Partnership With:

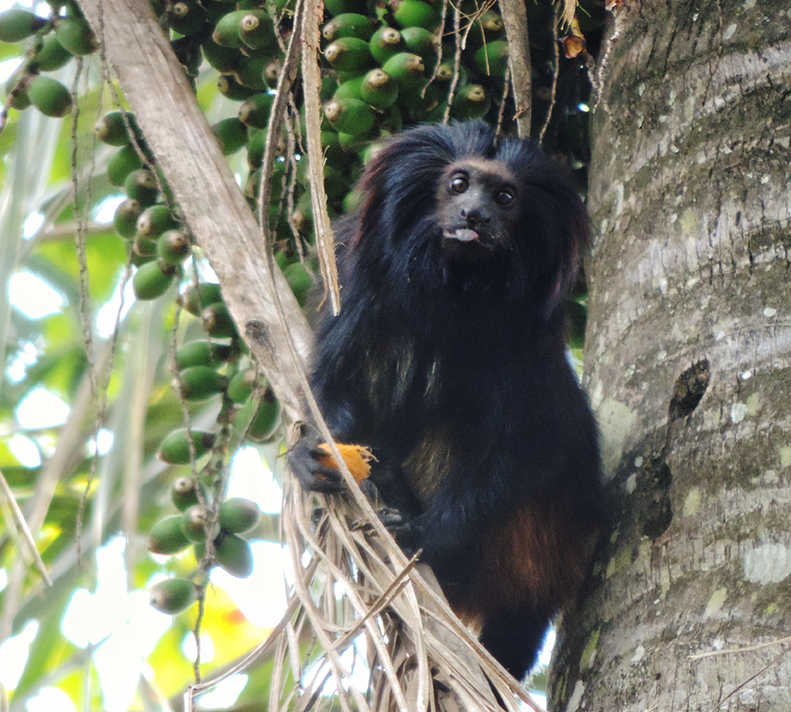
Black Lion Tamarin
Once stretched along Brazil’s southeast coast, the Atlantic Forest is now a green archipelago; less than 30 percent of its original canopy remains. In these islands of trees, the black lion tamarin (Leontopithecus chrysopygus), a primate found nowhere else on Earth, clings to survival. With fewer than 1,600 individuals left, this Endangered species is a symbol of hope for one of the world’s most biodiverse ecosystems. The Instituto de Pesquisas Ecológicas (IPÊ), with support from the Colossal Foundation’s Species Reintroduction Fund, is working to secure a future for the tamarins through population management, habitat restoration, and community engagement in São Paulo’s Pontal do Paranapanema region.
Learn More
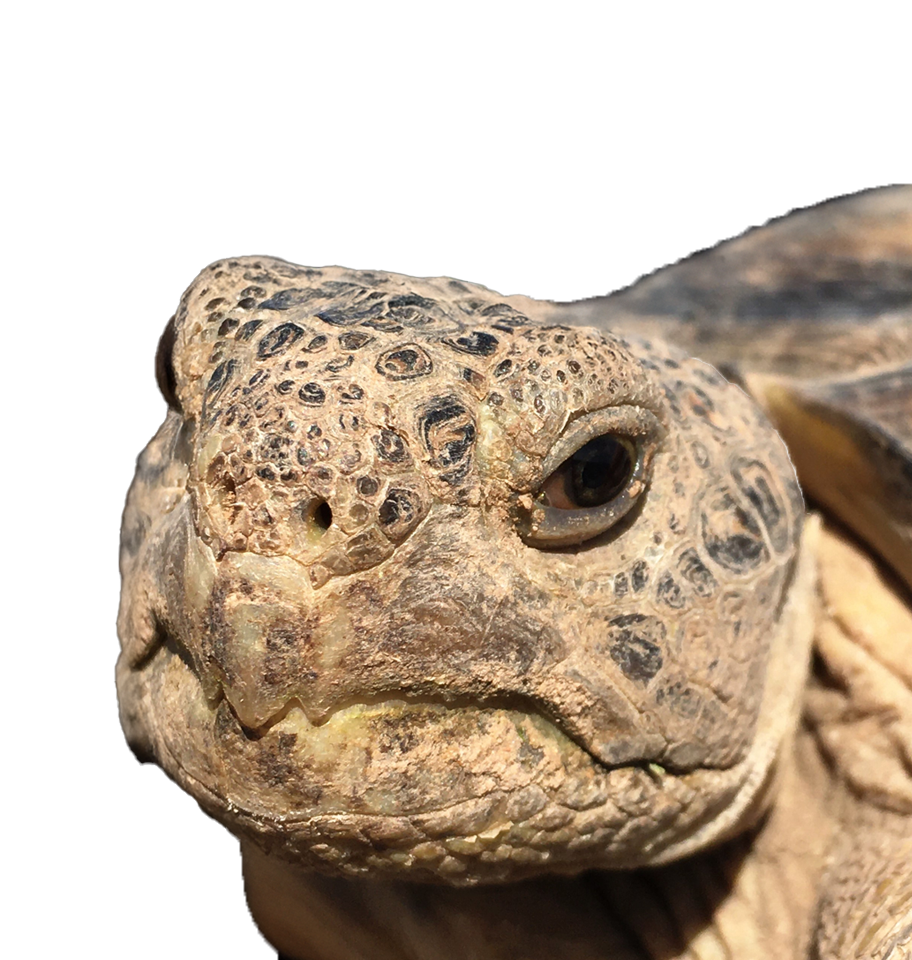

Bolson Tortoise
Gopherus flavomarginatus
- Estimated Population: 2,500
- Class: Reptilia
- Order: Testudines
- Family: Testudinidae
- Genus: Gopherus
 [ Status : Critically Endangered ]
[ Status : Critically Endangered ]


Population Threats
 Habitat Loss
Habitat Loss Illegal Pet Trade
Illegal Pet Trade Predation by Introduced Species
Predation by Introduced Species Climate Change
Climate Change Slow Reproductive Rate
Slow Reproductive Rate
Our Programs
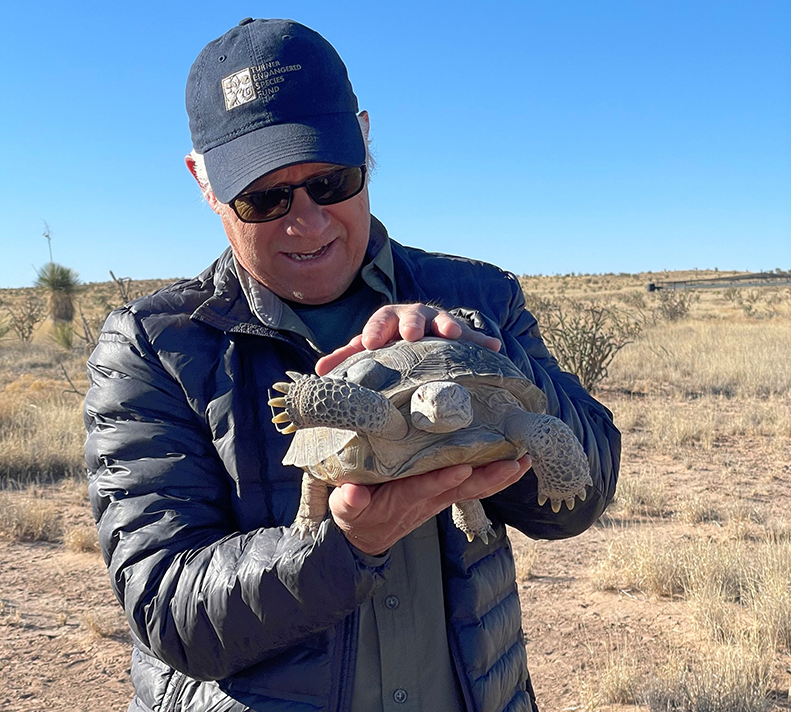

In Partnership With:

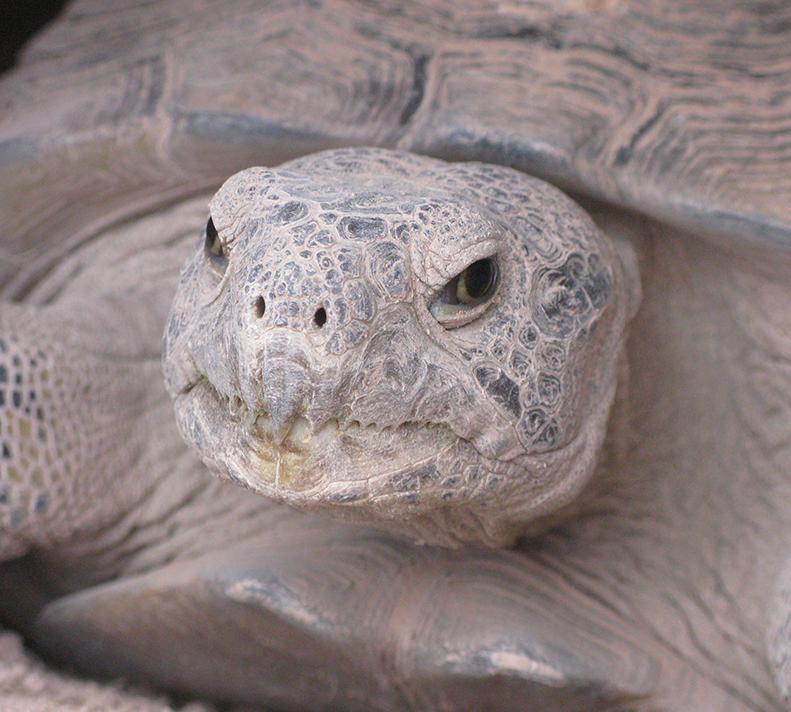
Bolson Tortoise
Beneath the sun-baked deserts of New Mexico, the Turner Endangered Species Fund (TESF) is bringing back a prehistoric relic—the Bolson Tortoise (Gopherus flavomarginatus). Once, these gentle giants lumbered across desert grasslands from the American Southwest into Mexico. Climate shifts and human pressure led to its vanishing from its United States range over 10,000 years ago. Today, the Bolson tortoise is listed as Critically Endangered, with a global wild population numbering less than 2,500 animals. Since 2006, TESF has been leading managed breeding and headstarting efforts, raising the first U.S.-born Bolson tortoise in 10,000 years, and begun releasing young tortoises onto vast, predator-managed grasslands.
Learn More
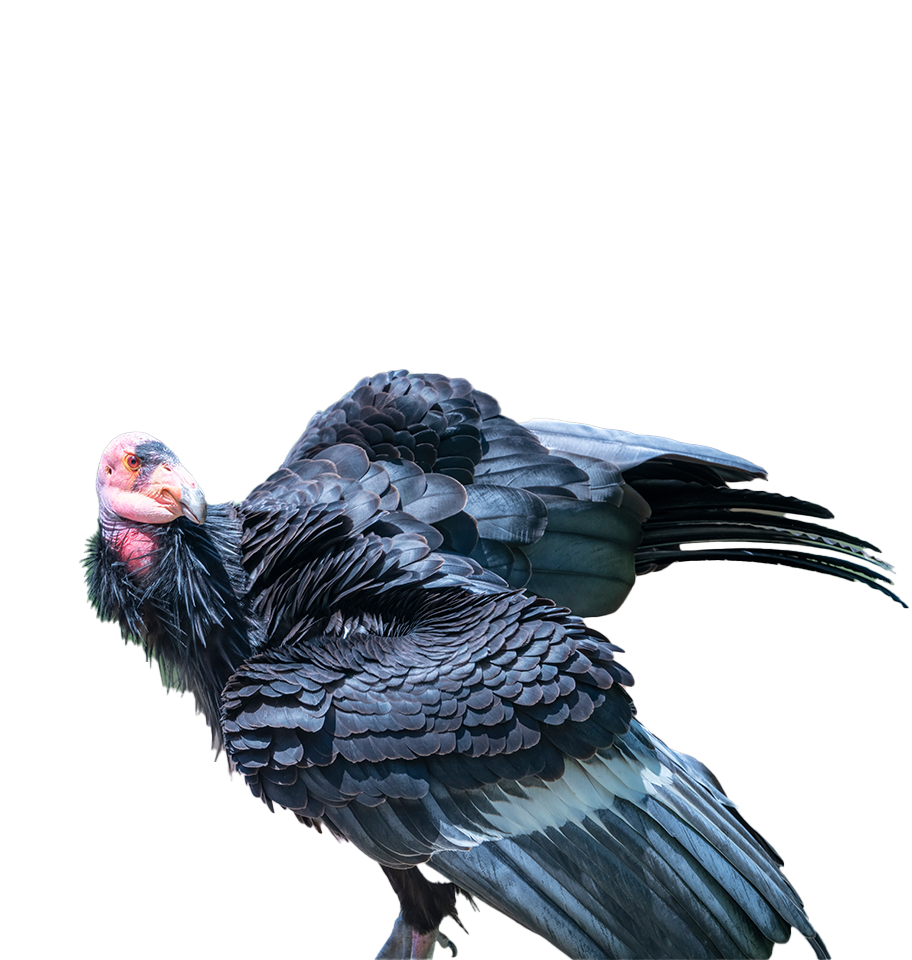

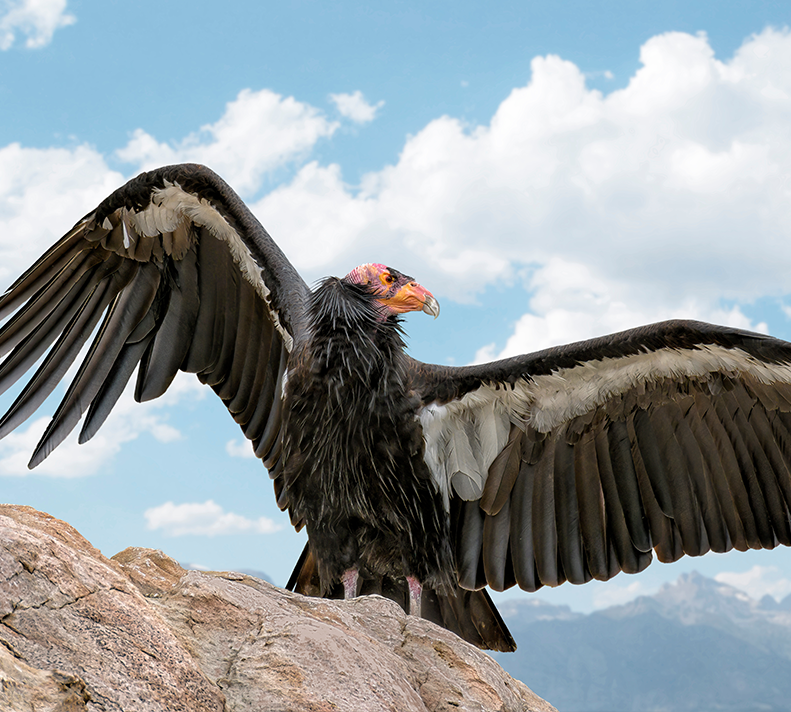
California Condor
Gymnogyps californianus
- Estimated Population: ~340 wild birds
- Class: Aves
- Order: Accipitriformes
- Family: Cathartidae
- Genus: Gymnogyps
 [ Status : Critically Endangered ]
[ Status : Critically Endangered ]


Population Threats
 Lead poisoning from ingesting spent lead ammunition fragments
Lead poisoning from ingesting spent lead ammunition fragments Habitat loss and degradation
Habitat loss and degradation Microtrash ingestion by chicks, which can cause injury or death
Microtrash ingestion by chicks, which can cause injury or death Power line collisions and electrocutions
Power line collisions and electrocutions Low reproductive rate
Low reproductive rate Historical overhunting and poisoning
Historical overhunting and poisoning
Our Programs
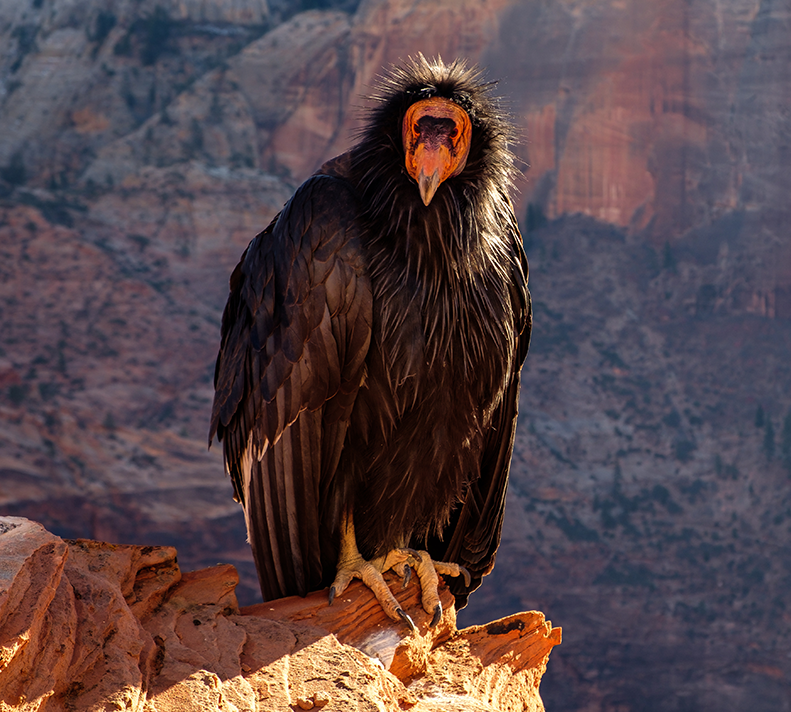

In Partnership With:

California Condor
The colossal 10-foot wingspan of the qú’nes (condor) once shadowed the sheer walls of Hells Canyon, North America’s deepest gorge and a sacred part of the Nez Perce homeland. The California condor (Gymnogyps californianus), now Critically Endangered, has been absent here for more than a century. The Nez Perce Tribe’s Wildlife Division, with support from the Colossal Foundation’s Species Reintroduction Fund, is leading an effort to bring North America's largest land bird back to their ancestral homeland, reviving both an ecological cornerstone and a cultural touchstone.
Learn More
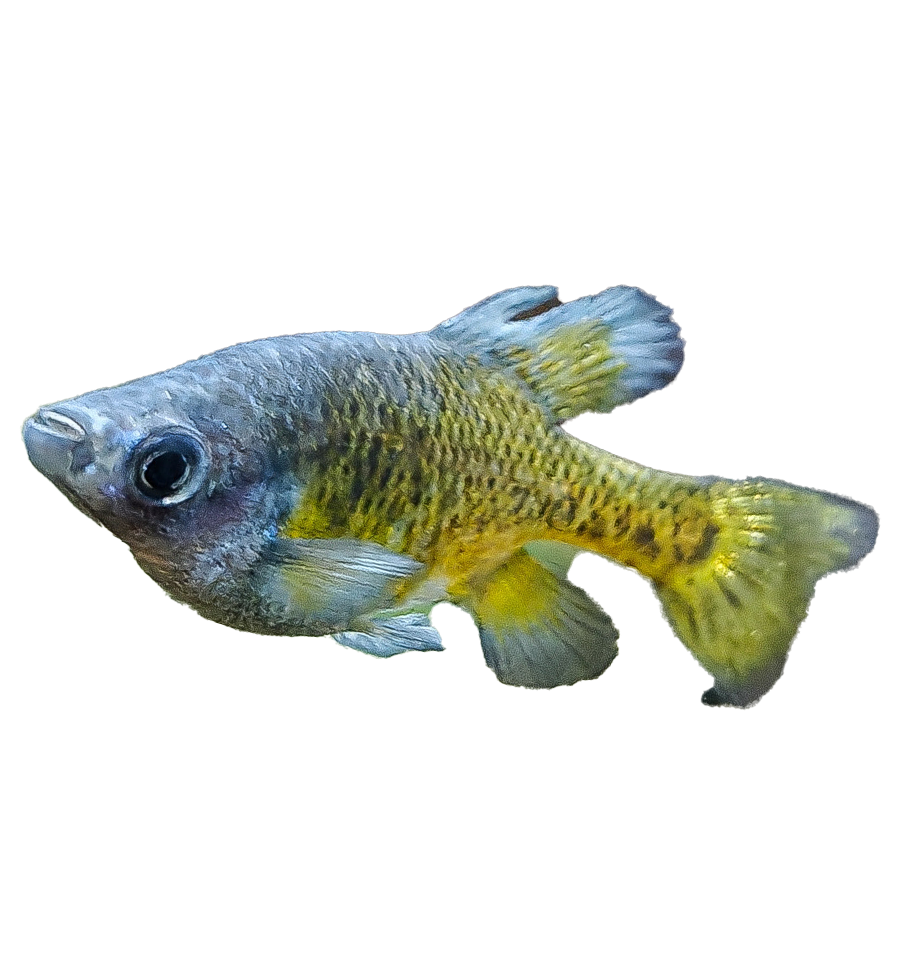

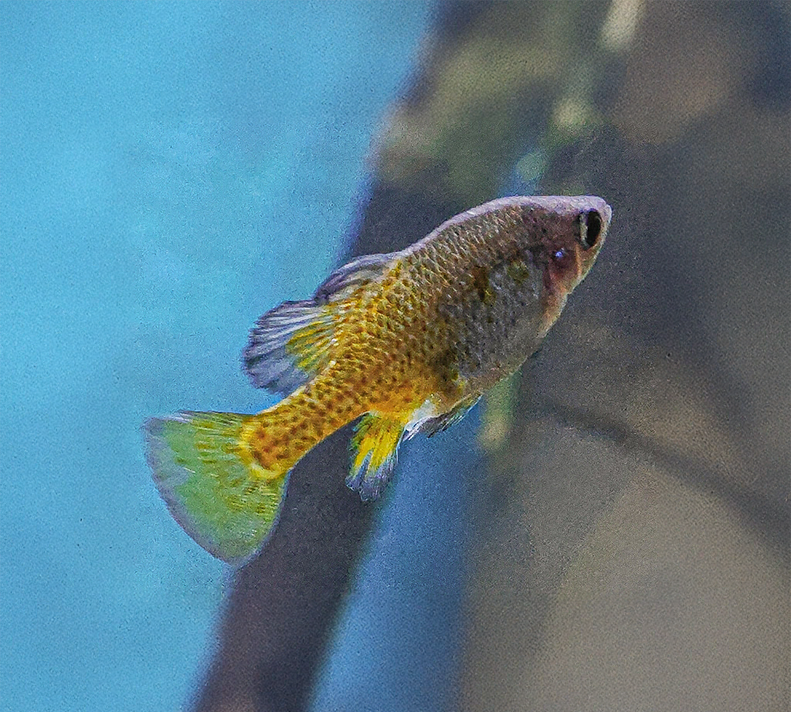
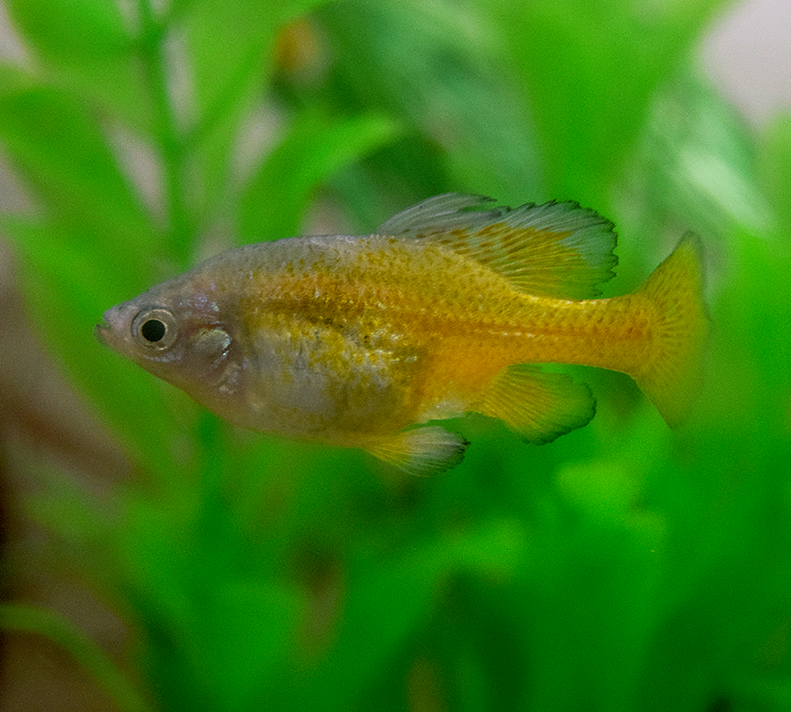
Golden Skiffia
Skiffia francesae
- Estimated Population: Extinct in the Wild
- Class: Actinopterygii
- Order: Cyprinodontiformes
- Family: Goodeidae
- Genus: Skiffia
 [ Status : Extinct in the Wild ]
[ Status : Extinct in the Wild ]


Population Threats
 Habitat loss and degradation from water pollution and water diversion
Habitat loss and degradation from water pollution and water diversion Invasive species competing for resources
Invasive species competing for resources Small, isolated populations vulnerable to environmental changes
Small, isolated populations vulnerable to environmental changes
Our Programs

In Partnership With:

Golden Skiffia
Mexico’s golden skiffia (Skiffia francesae) disappeared from the wild a generation ago, its spring-fed pools choked by pollution and invasive fish. Today the species clings to existence in a captive hatchery program, where scientists have preserved precious individuals that hold the promise of species survival. Now, the Universidad Michoacana de San Nicolás de Hidalgo, with support from the Colossal Foundation’s Species Reintroduction Fund, is working to bring this Extinct-in-the-Wild species back, alongside two other Extinct-in-the-Wild fish, the banded allotoca (Allotoca goslinei) and the Ameca shiner (Notropis amecae). By coupling species reintroduction with large-scale habitat renewal and local stewardship, this project aims to recreate a self-sustaining, native-dominated fish community, and a model for freshwater recoveries across Mexico.
Learn More Northern Quoll
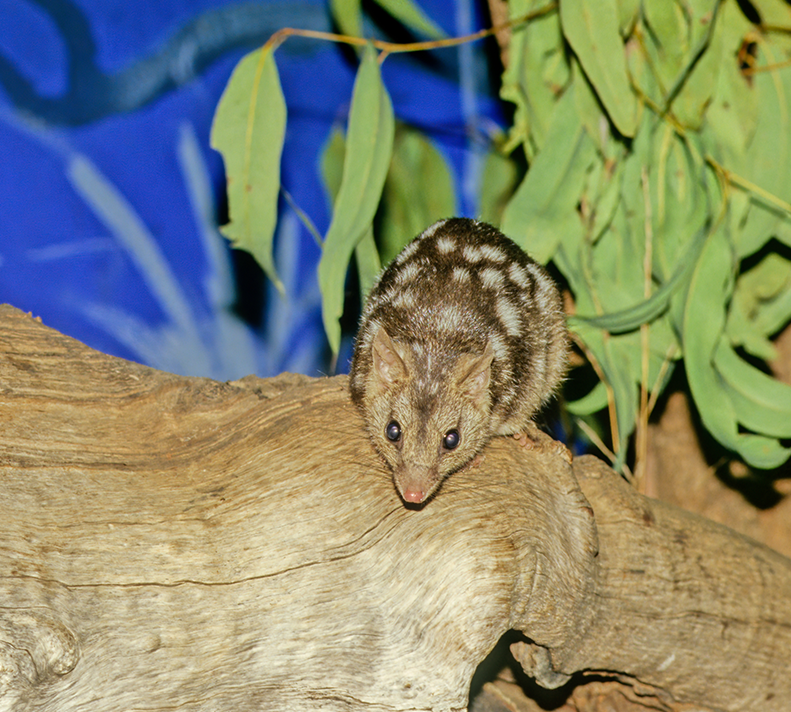
Northern Quoll
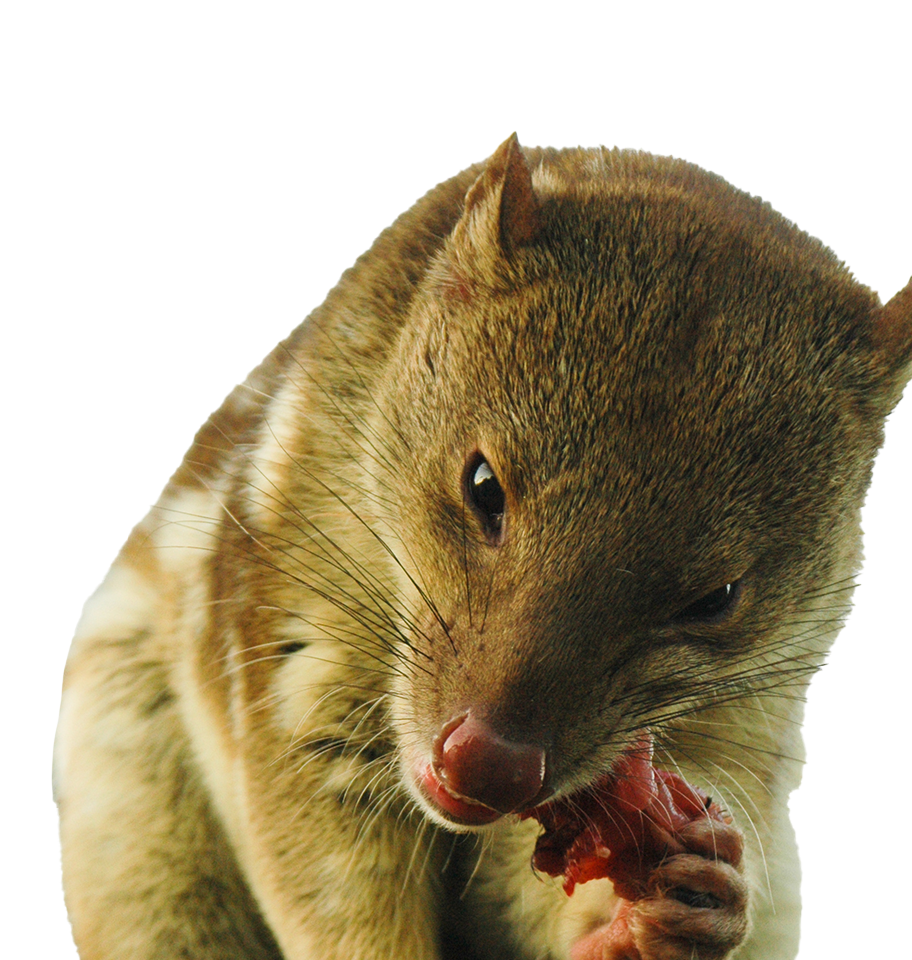


Northern Quoll
Dasyurus hallucatus
- Est. Current Population: 80,000
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Dasyuromorphia
- Family: Dasyuridae
- Genus: Dasyurus
- Region: Northern Australia
- Avg. Length (w/o tail): 25–37 cm | 9.8–15 in
- Avg. Weight: 350 - 1,120 g | 12 - 40 oz
 [ Status : Endangered ]
[ Status : Endangered ]


Population Threats
 Invasive Species (Cane Toads)
Invasive Species (Cane Toads) Habitat Loss
Habitat Loss
Our Programs

In Partnership With:

Engineering Cane Toad Resistance in Northern Quolls
The introduction of invasive cane toads to Australia has wreaked havoc on native marsupial predators who have suffered severe population declines due to the toad’s deadly toxins. One of the species that has suffered most is the Endangered northern quoll. This project uses advanced gene-editing technologies to introduce genetic resistance to cane toad toxin in northern quolls. By developing genetically resilient populations, the initiative aims to prevent the extinction of the northern quoll and restore ecological balance.
Learn More Northern White & Sumatran Rhinoceros
Northern White & Sumatran Rhinoceros
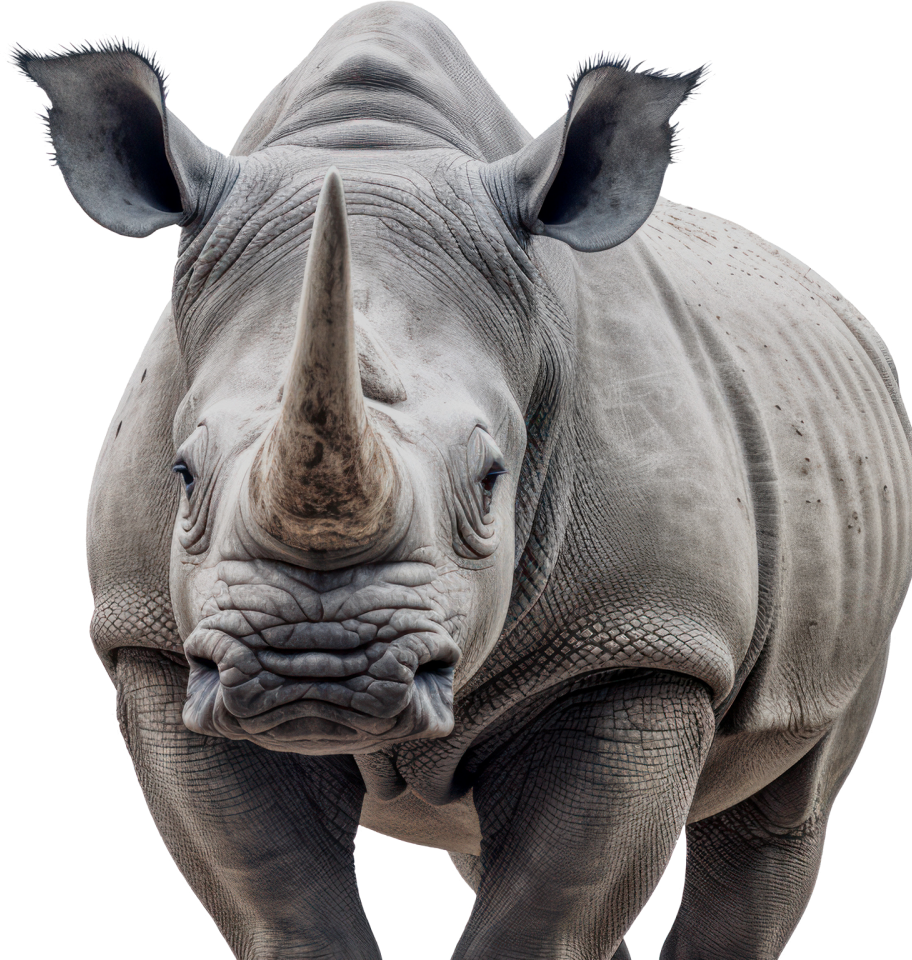


Northern White Rhino
Ceratotherium simum cottoni
- Est. Current Population: 2
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Perissodactyla
- Family: Rhinocerotidae
- Genus: Ceratotherium
- Region: Central African grasslands
- Avg. Length: 5 to 6 ft | 1.5 to 1.8 m
- Avg. Weight: 3080 to 7920 lb | 1.4 to 3.6 tons
 [ Status : Critically Endangered ]
[ Status : Critically Endangered ]


Population Threats
 HABITAT loss
HABITAT loss Poaching
Poaching


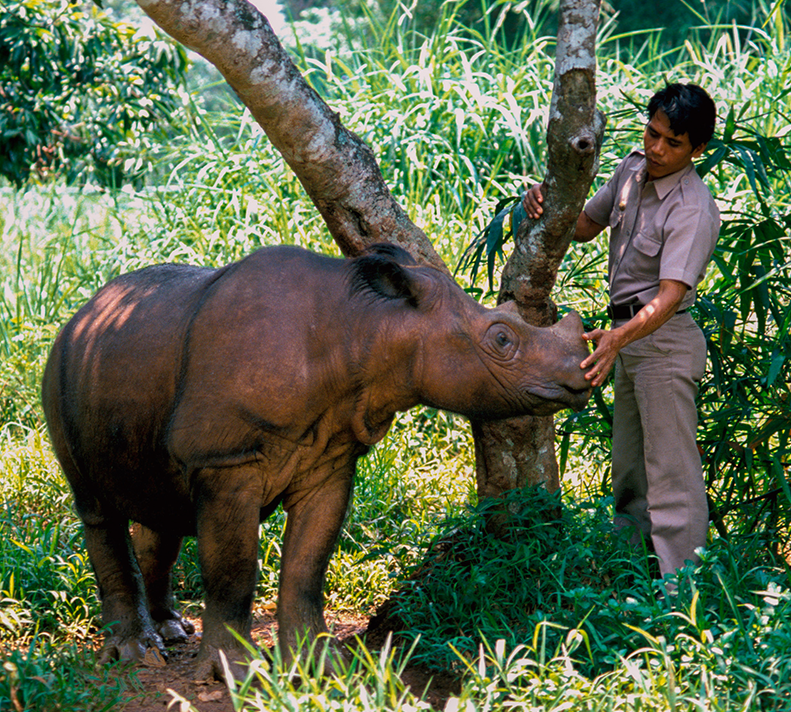
Sumatran Rhino
Dicerorhinus sumatrensis
- Est. Current Population: 40
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Perissodactyla
- Family: Rhinocerotidae
- Genus: Dicerorhinus
- Region: Central African grasslands
- Avg. Length: 3.3-5 ft | 6.5-13 feet
- Avg. Weight: 1,320 -2,090 lb | 0.66 to 1.05 tons
 [ Status : CRITICALLY ENDANGERED ]
[ Status : CRITICALLY ENDANGERED ]


Population Threats
Habitat Loss
 Poaching
Poaching
Our Programs

In Partnership With:

Engineering a Future for the Northern White Rhino
Colossal joins BioRescue for the Northern White Rhino project, sequencing viable museum samples to restore genetic diversity. Gene editing tools are being developed to enhance cell lines for embryo transfer, ensuring the restoration of lost genetic diversity.
Learn More
In Partnership With:



Protecting Sumatran Rhinos from Extinction
The Critically Endangered Sumatran rhino faces severe population declines due to habitat loss and low genetic diversity. This collaboration seeks to enhance existing breeding programs and leverage genetic sequencing and assisted reproductive technologies to support and increase the population of rhinos in Indonesia.
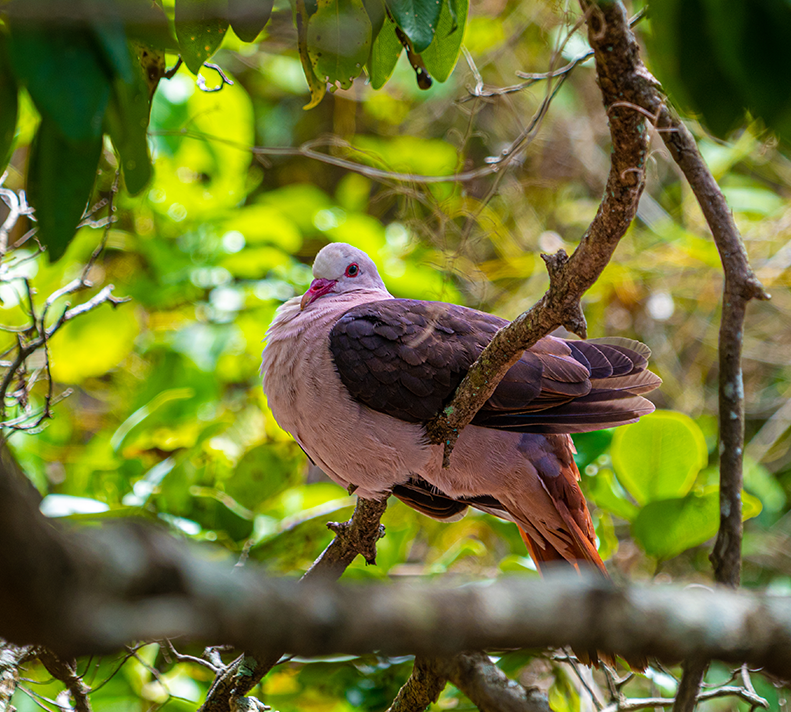
Learn More Pink Pigeon
Pink Pigeon
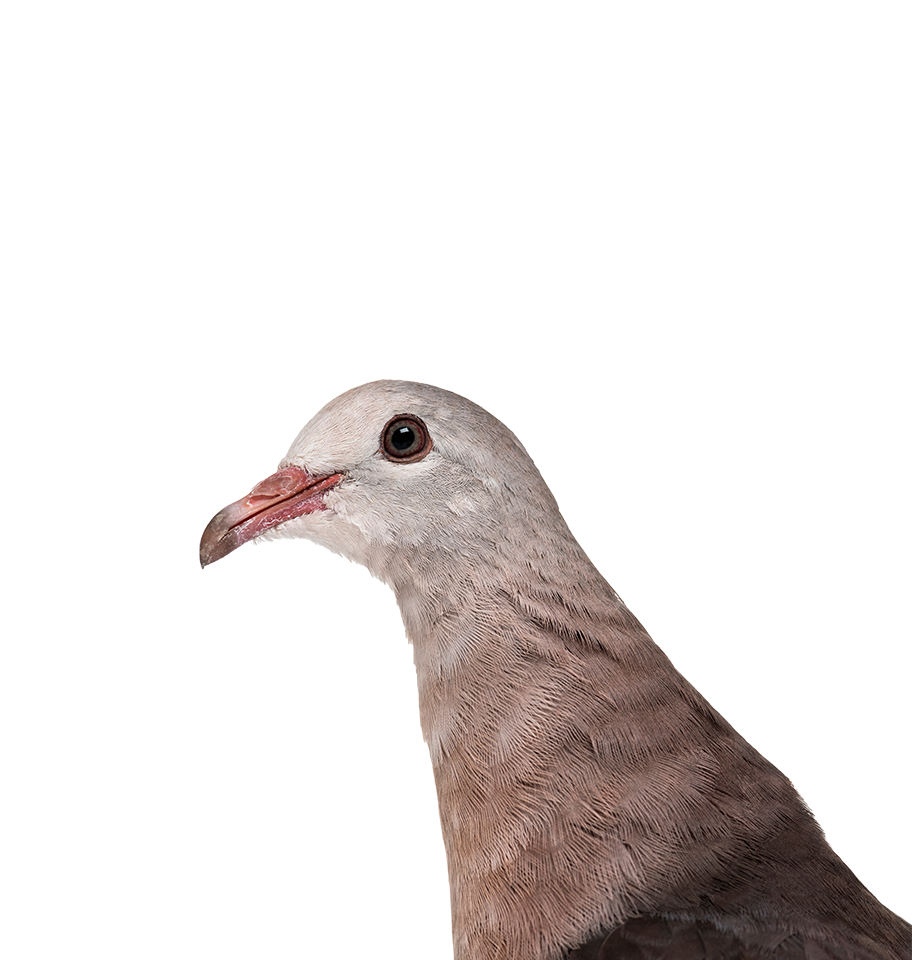


Pink Pigeon
Nesoenas mayeri
- Est. Current Population: 500
- Class: Aves
- Order: Columbiformes
- Family: Columbidae
- Genus: Nesoenas
- Region: Mauritius
- Avg. Length: 36–38 centimetres | 14–15 in
- Avg. Weight: 350 grams
 [ Status : Vulnerable ]
[ Status : Vulnerable ]


Population Threats
 Habitat Loss
Habitat Loss  Disease
Disease Genetic Erosion
Genetic Erosion
Our Programs

In Partnership With:


Pink Pigeon Genetic Rescue
The pink pigeon, a bird native to the island of Mauritius, faces extinction in coming decades due to severe genetic erosion. This project employs cutting-edge gene editing techniques to genetically rescue the pink pigeon and reintroduce historic diversity into today’s population. Utilizing preserved DNA from museum specimens, the initiative seeks to strengthen the genetic resilience of the charismatic species, ensuring its long-term viability.
Learn More
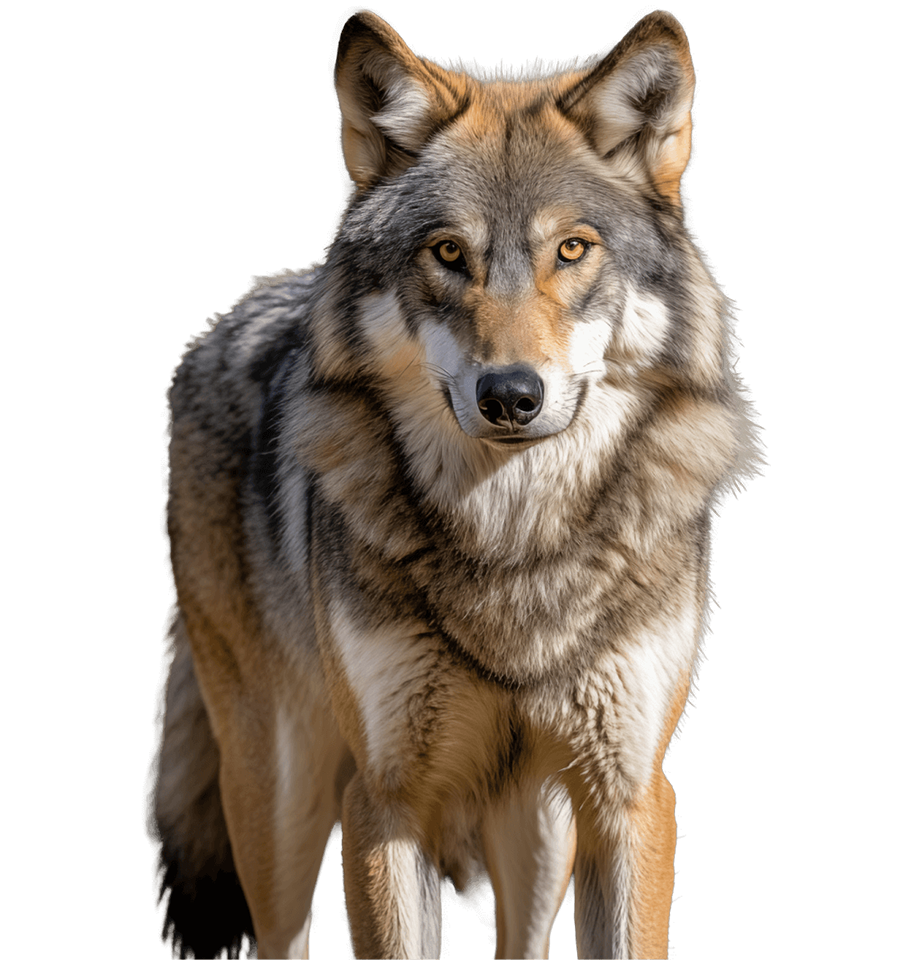

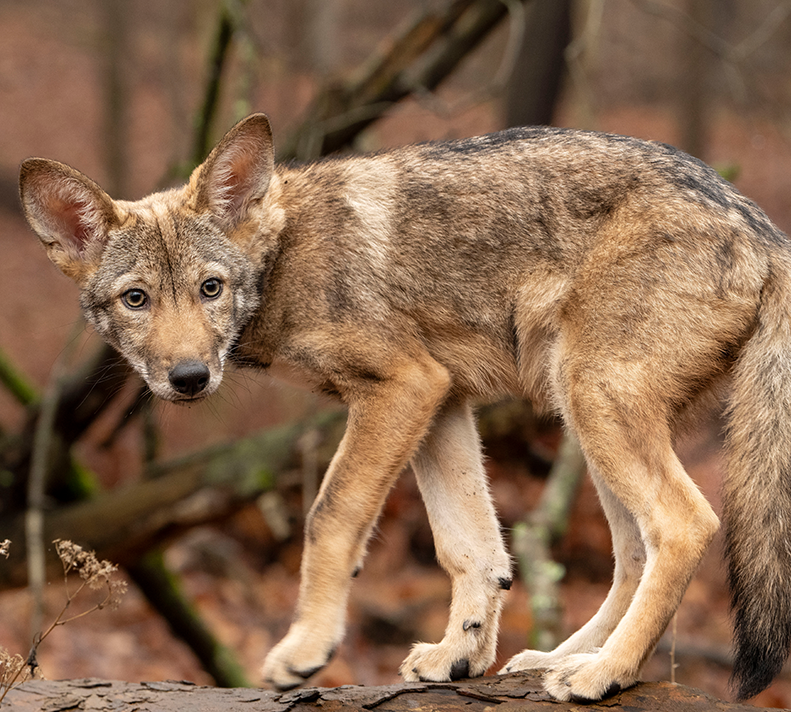
Red Wolf
Canis rufus
- 17 known wild individuals in North Carolina; around 200–270 in managed breeding programs
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Family: Canidae
- Genus: Canis
 [ Status : Critically Endangered ]
[ Status : Critically Endangered ]


Population Threats
 Habitat Loss & Fragmentation
Habitat Loss & Fragmentation Human-Wildlife Conflict
Human-Wildlife Conflict
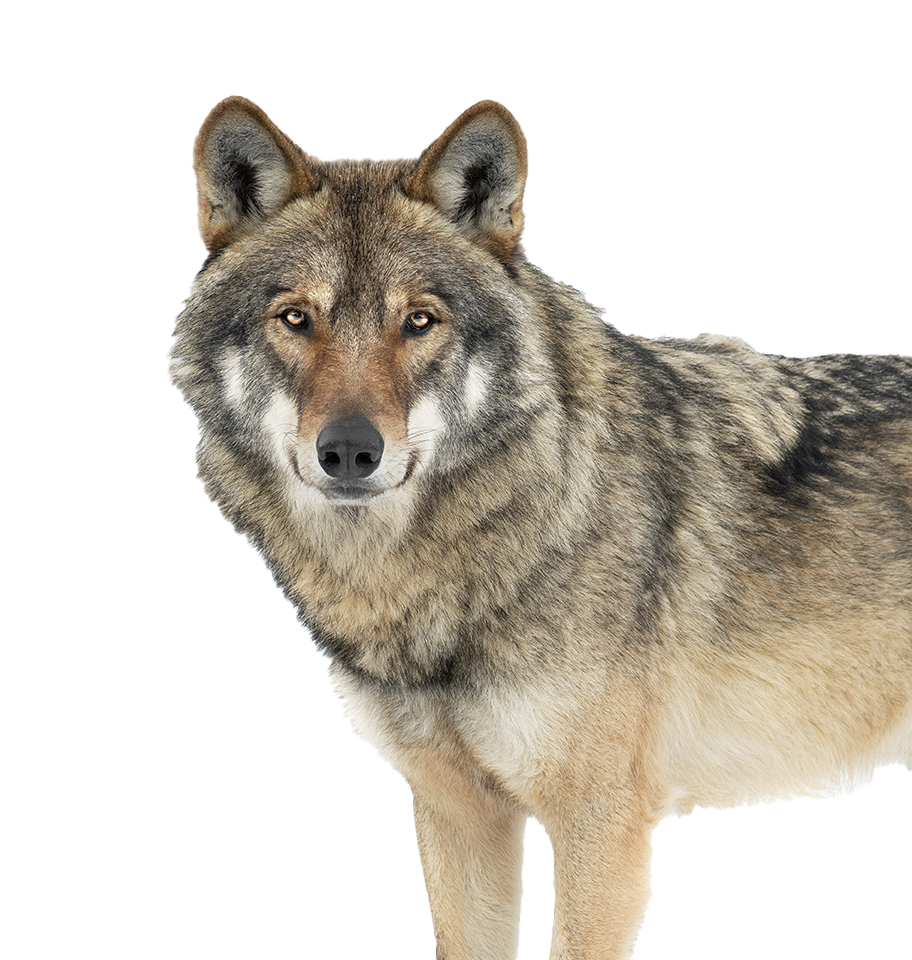


Gray Wolf
Canis lupus
- Estimated Current Population: ~200,000+ worldwide // 13,400-16,900 USA
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Family: Canidae
- Genus: Canis
 [ Status : Least Concern ]
[ Status : Least Concern ]
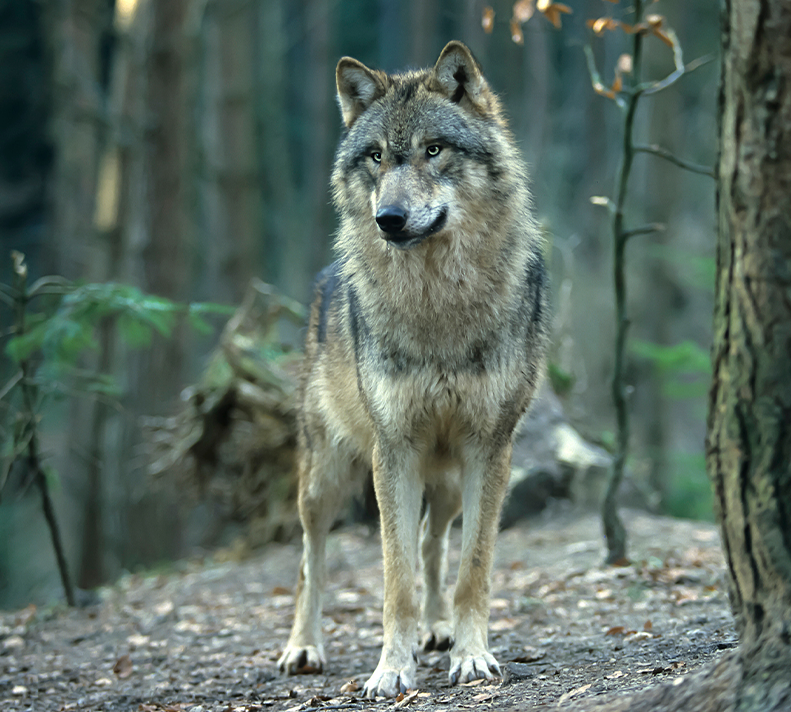


Population Threats
 Habitat Loss & Fragmentation
Habitat Loss & Fragmentation Human-Wildlife Conflict
Human-Wildlife Conflict
Our Programs

In Partnership With:



Restoring the Ancestral Red Wolf Through Genetic Rescue
The Ghost Wolf Genetic Rescue Initiative is a groundbreaking conservation project led by Colossal Biosciences, the Gulf Coast Canine Project, and local partners to restore the critically endangered American Red Wolf using the unique genetics of Gulf Coast "ghost wolves." By integrating advanced genomics, cloning, and gene editing, this project aims to rebuild the lost diversity of the ancestral Red Wolf and reintroduce it into its native Gulf Coast habitat.
Learn More
In Partnership With:



Decoding the Howl: Using AI to Understand the Language of Yellowstone’s Wolves
Partnering with Yellowstone Forever, the official nonprofit partner of Yellowstone National Park, the Colossal Foundation is supporting the Yellowstone Wolf Project through an ambitious new bioacoustics initiative. This collaboration aims to revolutionize how conservationists monitor and protect wild wolf populations by integrating cutting-edge acoustic sensing, machine learning, and continuous ecological data collection across wolf territories in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem.
Learn More Tooth-Billed Pigeon
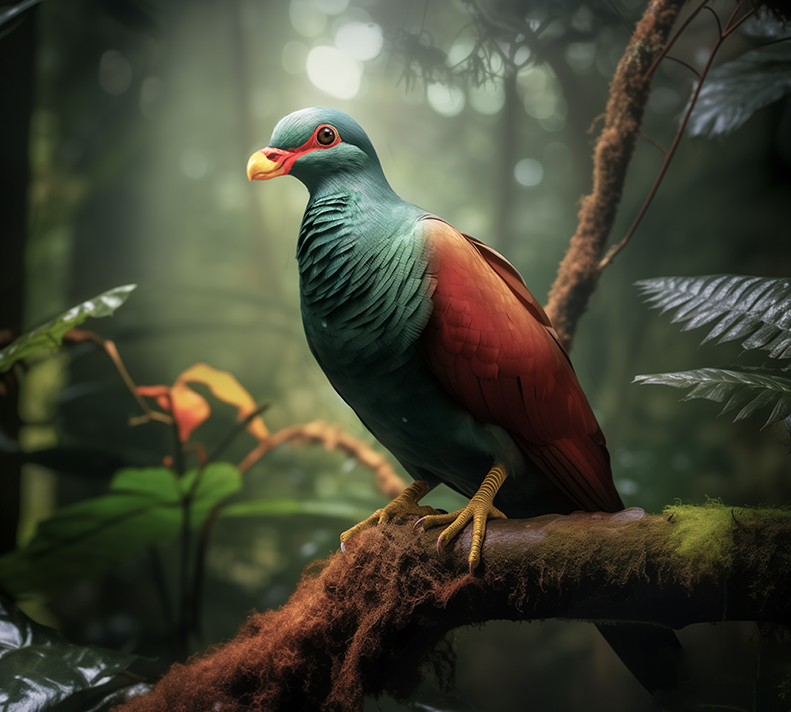
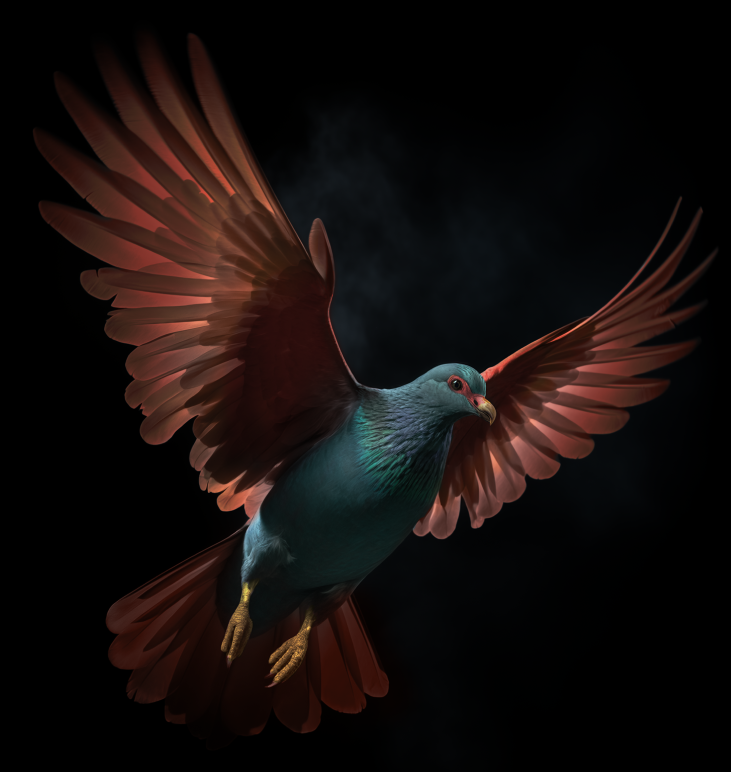
Tooth-Billed Pigeon
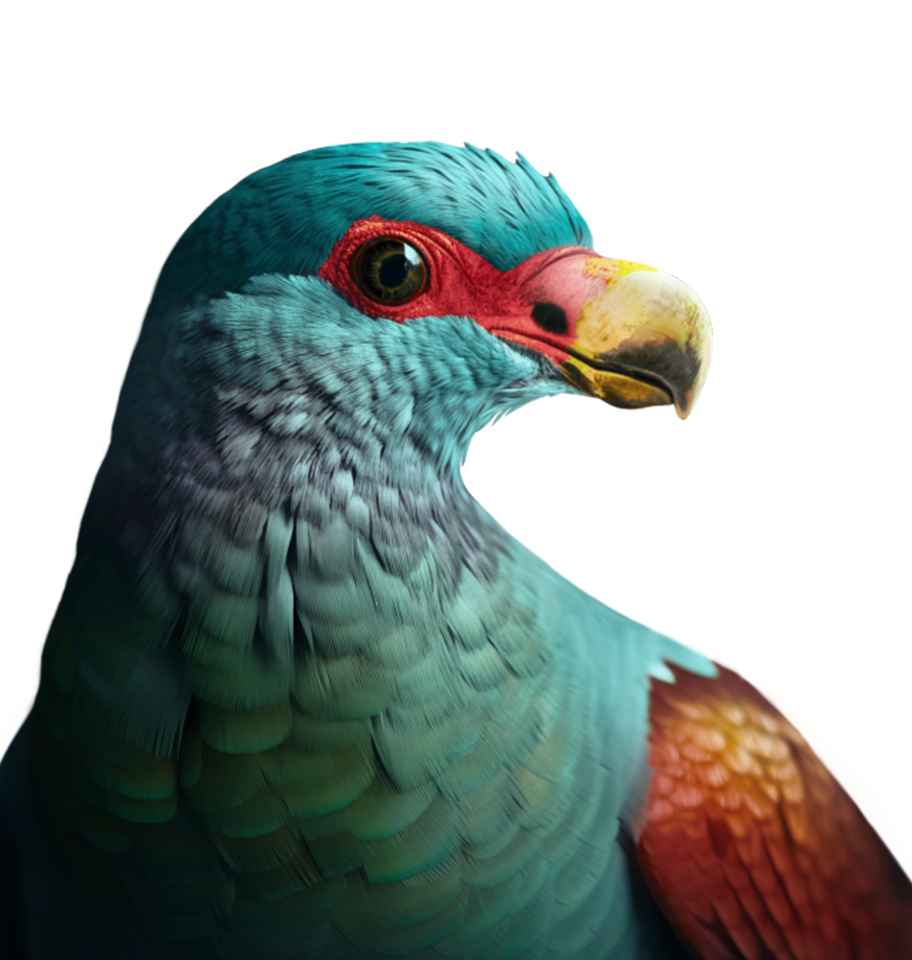


Tooth-Billed Pigeon
Didunculus strigirostris
- Est. Current Population: 70 - 380
- Class: Aves
- Order: Columbiformes
- Family: Columbidae
- Genus: Didunculus
- Region: Samoa
- Avg. Length: 31 cm
- Avg. Weight: 400 g
 [ Status : Critically Endangered ]
[ Status : Critically Endangered ]


Population Threats
habitat loss
 Hunting
Hunting Invasive Species
Invasive Species

In Partnership With:



Searching for the Lost Tooth-Billed Pigeon
This elusive tooth-billed pigeon, also known as the “little dodo,” is a bird native to the island of Samoa. It is classified as Critically Endangered and has not had a confirmed sighting since 2013. This collaboration is working to develop an A.I.-powered bioacoustic monitoring system aimed at locating the “lost” tooth-billed pigeon using the bird’s unique vocalization.
Learn More Vaquita
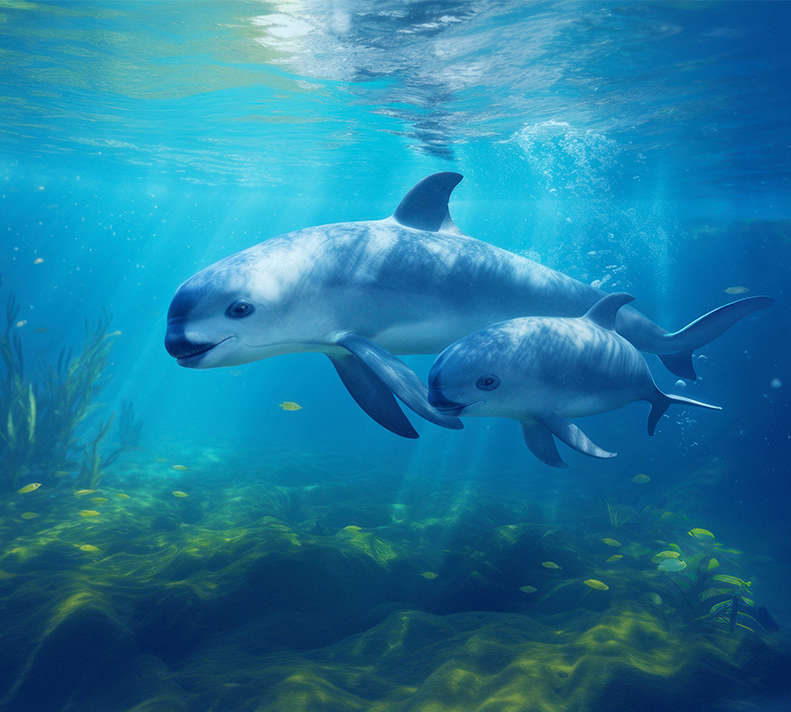
Vaquita
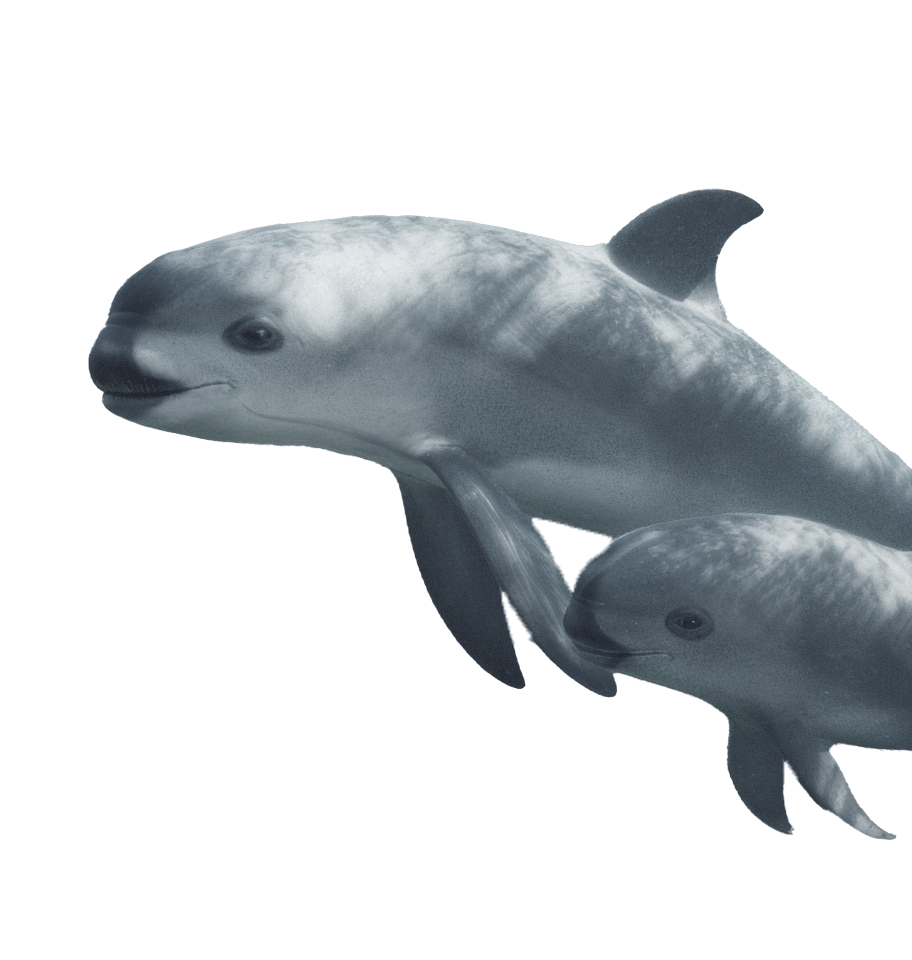


Vaquita
Phocoena sinus
- Est. Current Population: <10
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Artiodactyla
- Family: Phocoenidae
- Genus: Phocoena
- Region: Northern end of the Gulf of California
- Avg. Length: 150 cm (4.9 ft) (females) or 140 cm (4.6 ft) (males)
- Avg. Weight: 27 kg - 68 kg | 60 lb - 150 lb
 [ Status : Critically Endangered ]
[ Status : Critically Endangered ]


Population Threats
 Fisheries bycatch
Fisheries bycatch Habitat Loss
Habitat Loss Pollution
Pollution
Our Programs

Rescuing the Panda of the Sea
The vaquita is the world's smallest cetacean, and it is on the verge of extinction. With only a handful of vaquitas left, this project employs state-of-the-art monitoring techniques to track and study the remaining vaquitas in the Gulf of California. By analyzing this data, the initiative seeks to enhance conservation efforts and develop effective strategies to stabilize and increase the vaquita population.
Learn More
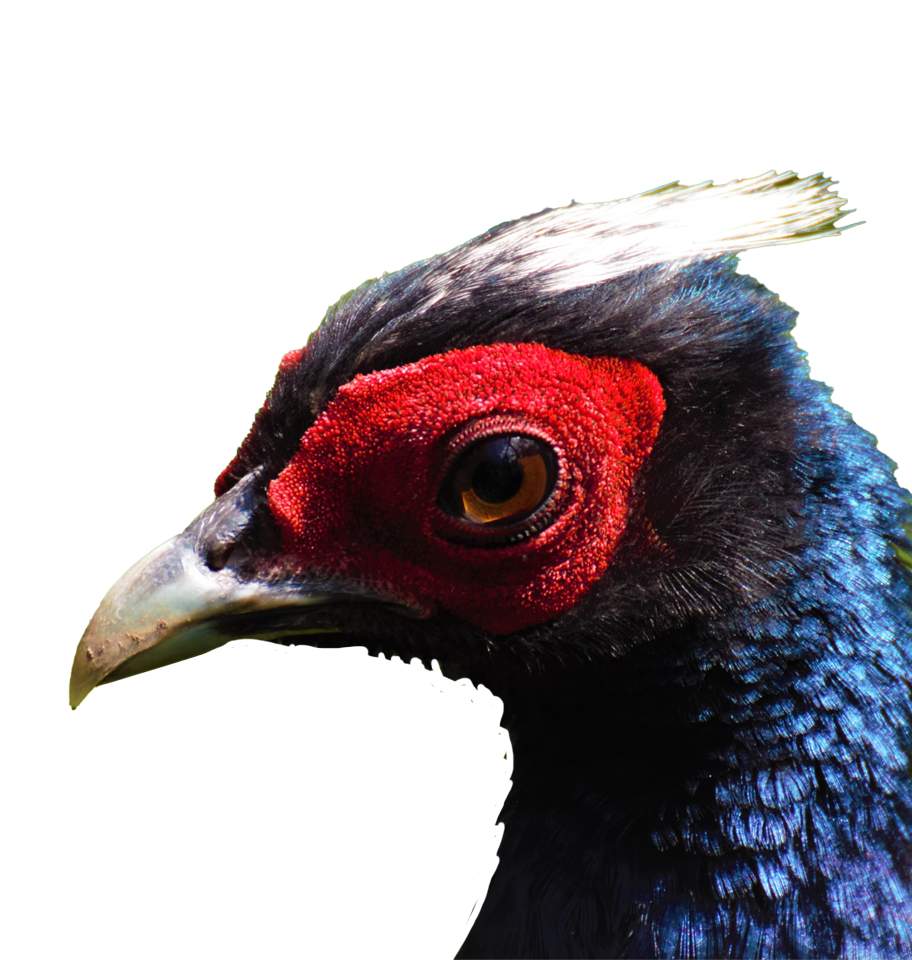

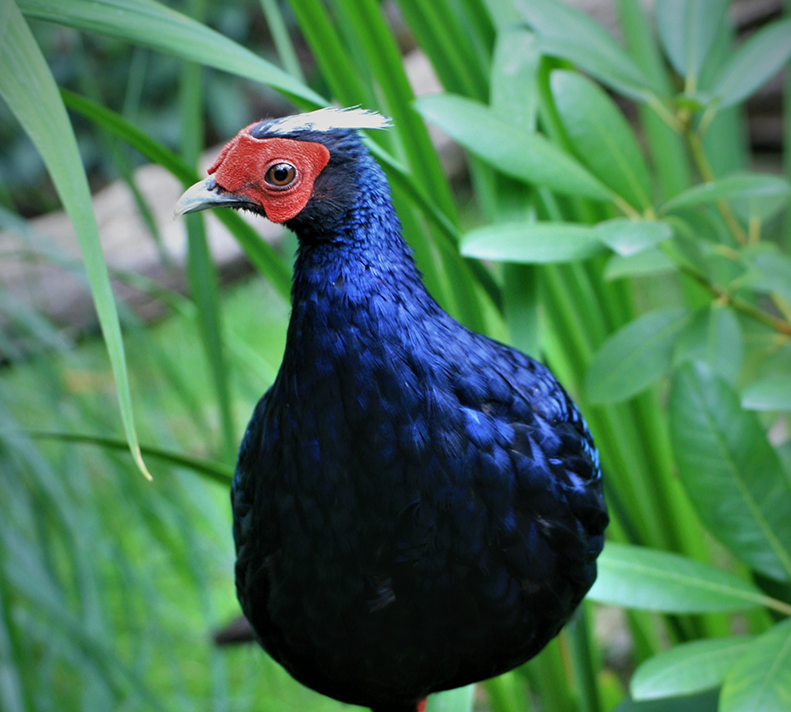
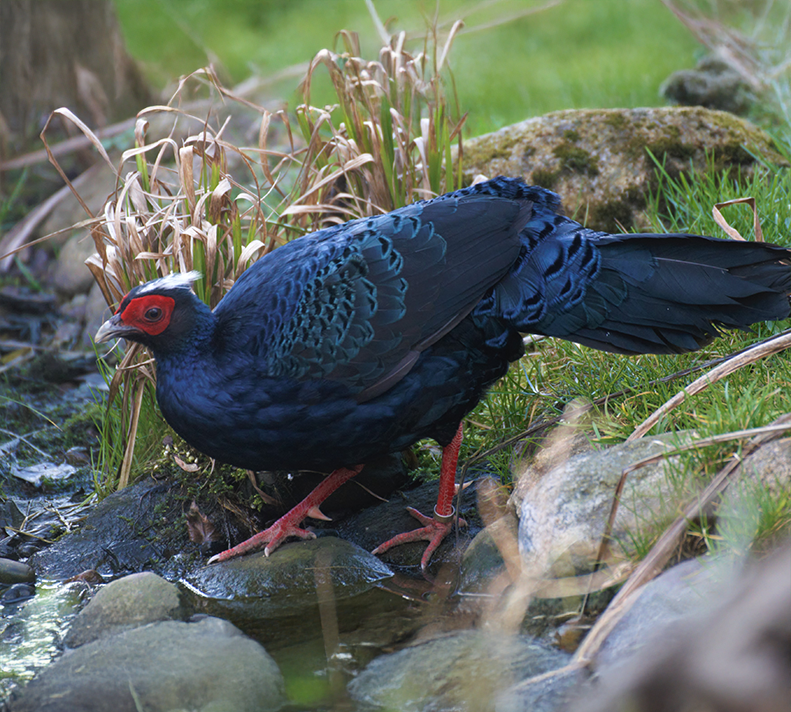
Vietnam Pheasant
Lophura edwardsi
- Estimated Population: Less than 500 left in zoos worldwide – possibly Extinct in the Wild
- Class: Aves
- Order: Galliformes
- Family: Phasianidae
- Genus: Lophura
 [ Status : Critically Endangered ]
[ Status : Critically Endangered ]


Population Threats
 Deforestation and habitat fragmentation due to logging and agriculture
Deforestation and habitat fragmentation due to logging and agriculture Hunting and trapping for food and trade
Hunting and trapping for food and trade Extremely small population size and limited genetic diversity
Extremely small population size and limited genetic diversity
Our Programs

In Partnership With:


Vietnam Pheasant
Once abundant in the lowland evergreen forests of central Vietnam, the Vietnam pheasant (Lophura edwardsi) has not been confirmed in the wild for two decades and is now listed as Critically Endangered—possibly Extinct in the Wild. With fewer than 500 Vietnam Pheasants left in zoos worldwide, this species teeters on the edge of extinction. Led by the local NGO Viet Nature and ZSL, this project builds the final bridge between captive breeding efforts and reintroduction. It aims to release fit, predator-savvy pheasants into protected forest reserves in Quang Binh Province, reviving a flagship species and the unique ecosystem it once shaped.
Learn More Victorian Grassland Earless Dragon
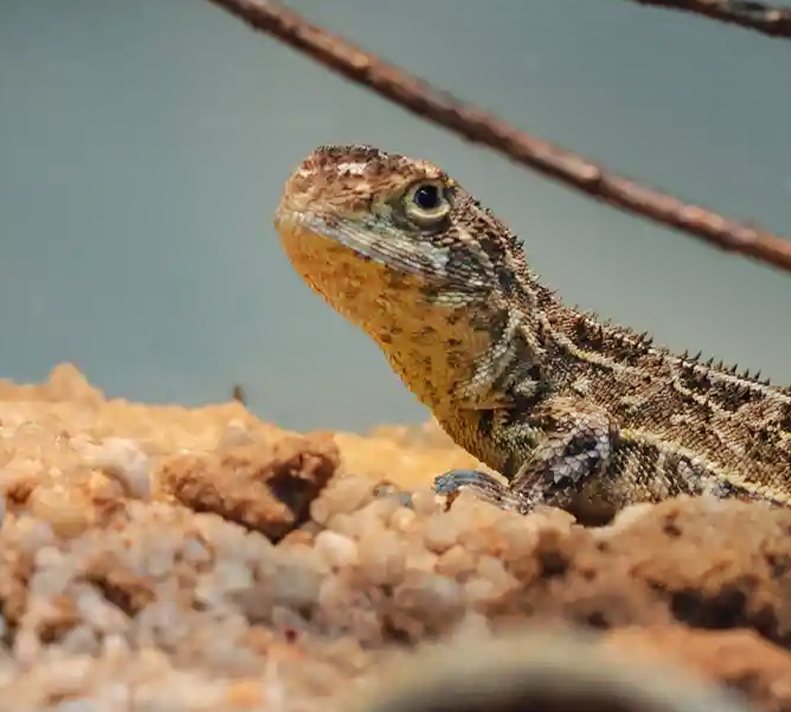
Victorian Grassland Earless Dragon
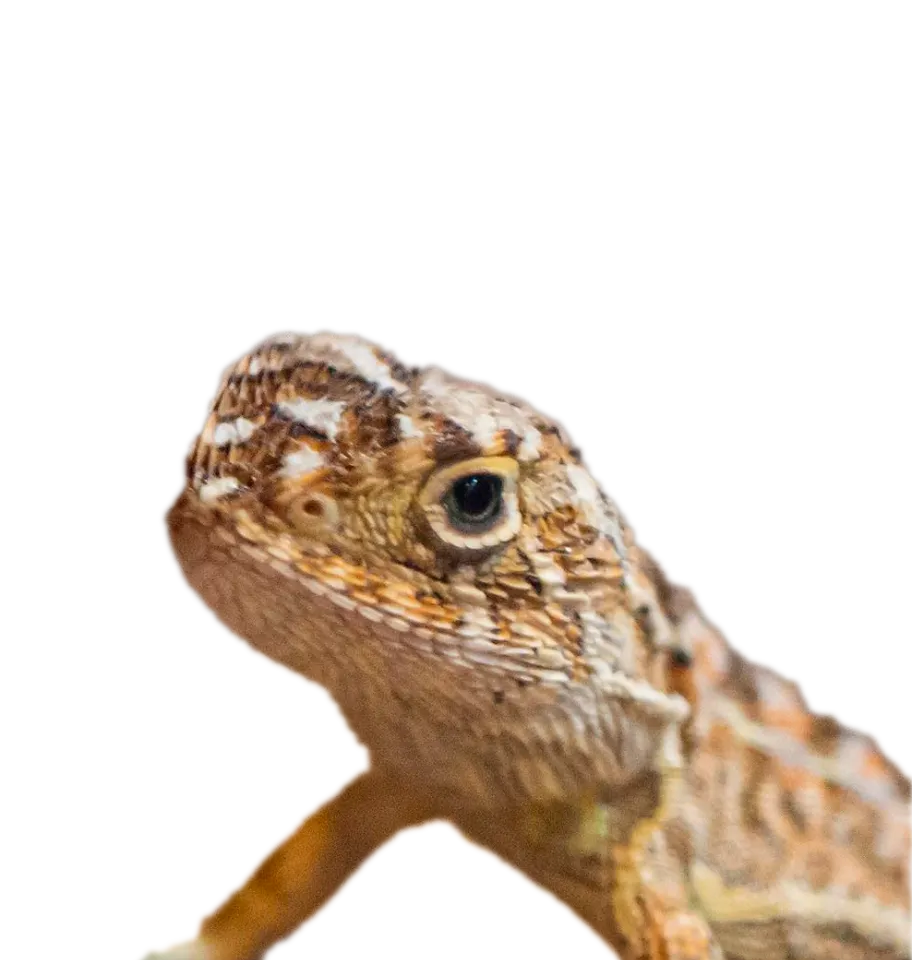


Victorian Grassland Earless Dragon
Tympanocryptis pinguicolla
- Est. Current Population: 120
- Class: Reptilia
- Order: Squamata
- Family: Agamidae
- Genus: Tympanocryptis
- Region: Australia
- Avg. Length: 12 - 15cm
- Avg. Weight: 5–9 grams
 [ Status : Critically Endangered ]
[ Status : Critically Endangered ]


Population Threats
 Habitat Loss
Habitat Loss
Our Programs

In Partnership With:

Rediscovering the Victorian Grassland Earless Dragon
The Victorian Grassland Earless Dragon is a Critically Endangered Australian lizard that was rediscovered in 2023 after not being seen for over 40 years. This project established an interim insurance and conservation breeding program for the recovered dragon population, and utilizes cutting-edge genomic technology to stabilize and grow its population.
Learn More
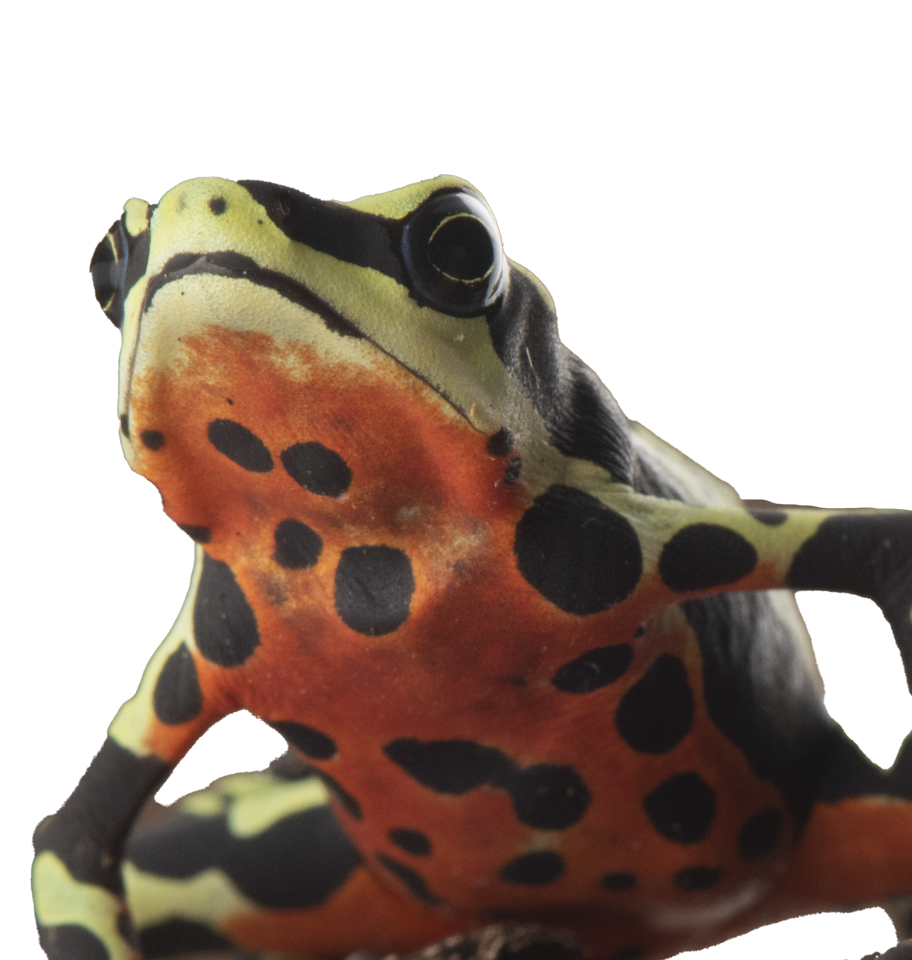

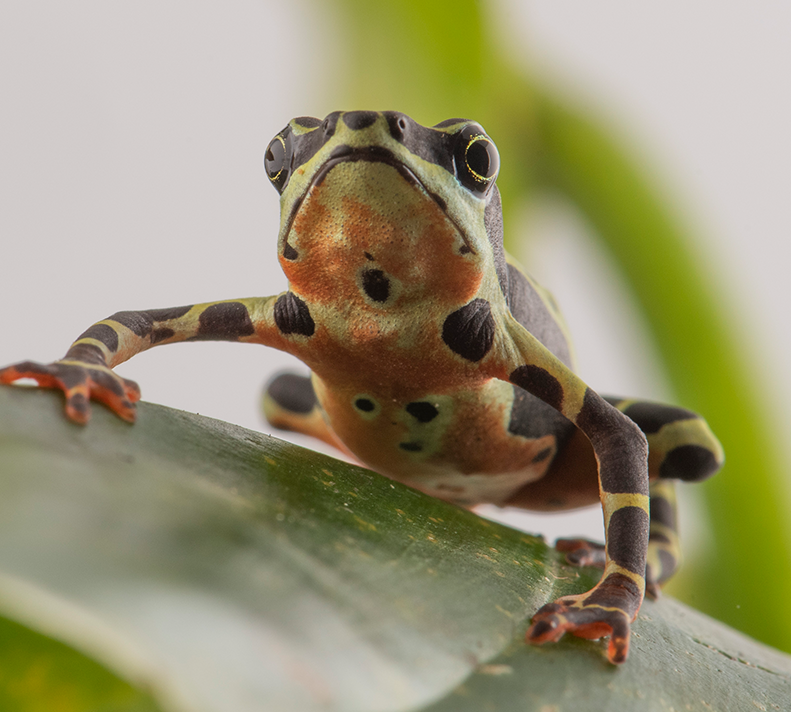
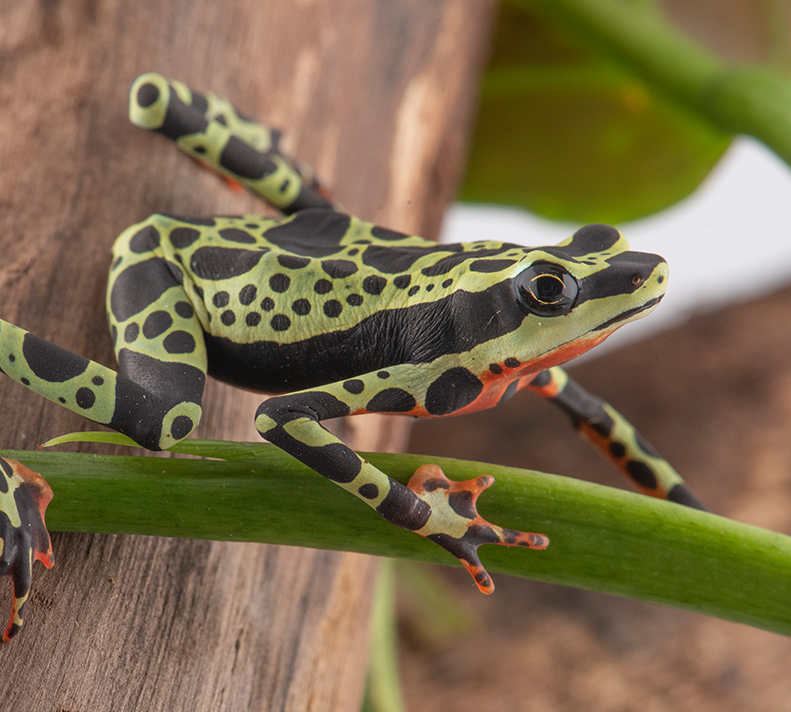
Wampukrum Harlequin Frog
Atelopus aff. spumarius
- Estimated Population: Unknown
- Class: Amphibia
- Order: Anura
- Family: Bufonidae
- Genus: Atelopus
 [ Status : Not formally listed ]
[ Status : Not formally listed ]


Population Threats
 Habitat loss from deforestation and agricultural expansion
Habitat loss from deforestation and agricultural expansion Chytrid fungus ( deadly amphibian disease)
Chytrid fungus ( deadly amphibian disease) Climate change affecting highland forest ecosystems
Climate change affecting highland forest ecosystems Limited data, making conservation planning more challenging
Limited data, making conservation planning more challenging
Our Programs

In Partnership With:

Harlequin Frog
Hidden for millennia in the misty headwaters of the Ecuadorian Amazon, the Wampukrum harlequin frog (Atelopus aff. spumarius) vanished from Quebrada de Napinaza after 2009, battered by mining, habitat loss, and the deadly chytrid fungus. Today the stream is finally protected, and Centro Jambatu’s scientists are ready to reintroduce this iconic amphibian. Over the next year they will breed, transport, and release more than 800 tadpoles, juveniles, and adults—the first step toward rebuilding a vibrant, self-sustaining population in Morona Santiago Province.
Learn More